Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Generating and Visualizing Signal Data#
- This example demonstrates how to:
Generate synthetic signals with up to 3 Gaussian pulses.
Compute a Region of Interest (ROI) mask based on pulse positions.
Visualize signals with peak positions, amplitudes, and the ROI mask.
Imports#
from DeepPeak.signals import SignalDatasetGenerator
from DeepPeak import kernel
Generate Synthetic Signal Dataset#
We generate a dataset with NUM_PEAKS Gaussian pulses per signal. The peak amplitudes, positions, and widths are randomly chosen within specified ranges.
NUM_PEAKS = 3
SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 200
sample_count = 12
generator = SignalDatasetGenerator(n_samples=sample_count, sequence_length=SEQUENCE_LENGTH)
kernel = kernel.Lorentzian(
amplitude=(10, 300), # Amplitude range
position=(0.3, 0.7), # Peak position range
width=0.02,
)
dataset = generator.generate(
kernel=kernel,
n_peaks=(3, 3),
noise_std=0, # Add some noise
categorical_peak_count=False,
)
dataset.plot(number_of_columns=3, number_of_samples=9)
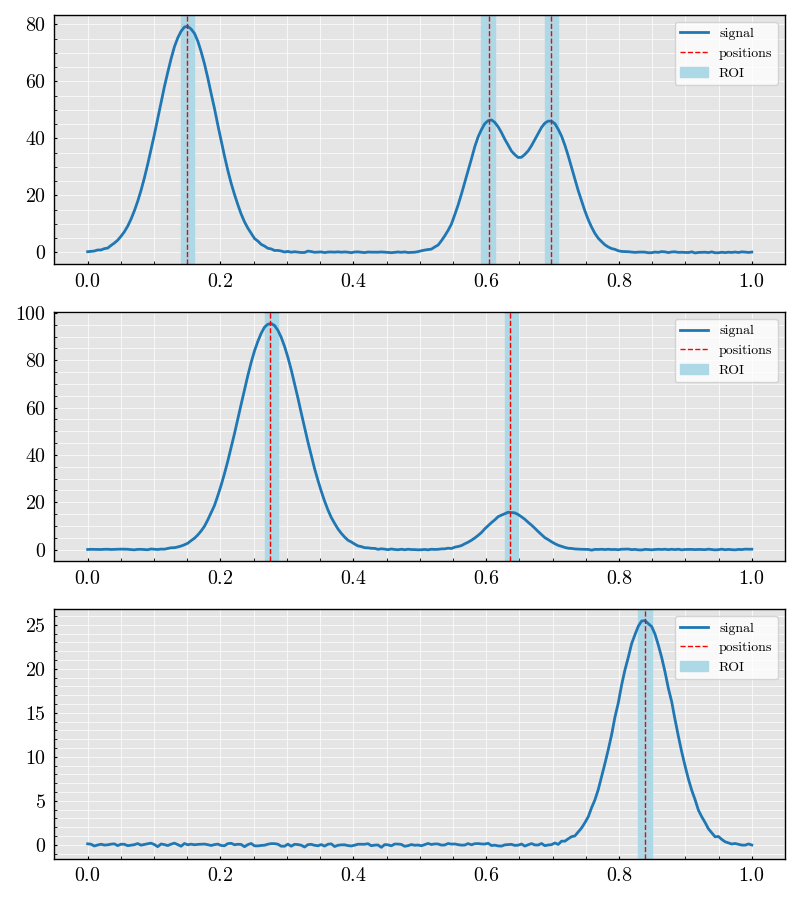
<Figure size 2400x900 with 9 Axes>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.992 seconds)