Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Non-Maximum Suppression for Gaussian Pulse Detection#
This example demonstrates the use of the NonMaximumSuppression class to detect Gaussian pulses in a one-dimensional signal. It generates a synthetic dataset of Gaussian pulses, applies the non-maximum suppression algorithm, and plots the results.
from DeepPeak.algorithms import NonMaximumSuppression
from DeepPeak.signals import SignalDatasetGenerator
from DeepPeak.kernel import Gaussian
NUM_PEAKS = 3
SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 400
generator = SignalDatasetGenerator(n_samples=6, sequence_length=SEQUENCE_LENGTH)
kernel = Gaussian(
amplitude=(10, 300), # Amplitude range
position=(0.3, 0.7), # Peak position range
width=0.02,
)
dataset = generator.generate(
kernel=kernel,
n_peaks=(3, 3),
noise_std=0, # Add some noise
categorical_peak_count=False,
)
print(dataset)
dataset.plot()
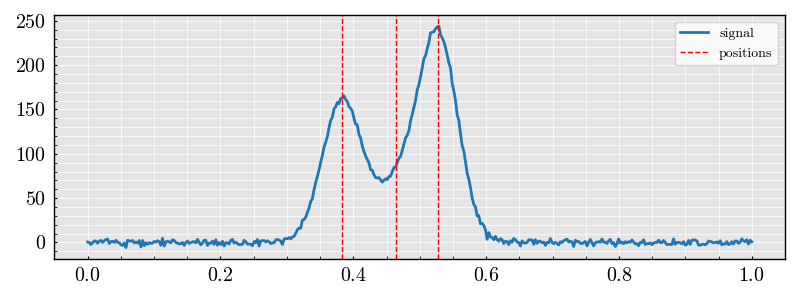
DataSet(signals, amplitudes, positions, widths, labels, x_values, num_peaks, region_of_interest)
<Figure size 800x900 with 3 Axes>
Configure and run the detector
peak_locator = NonMaximumSuppression(
gaussian_sigma=kernel.width,
threshold="auto",
maximum_number_of_pulses=5,
kernel_truncation_radius_in_sigmas=5,
)
result = peak_locator.run(time_samples=dataset.x_values, signal=dataset.signals[0])
batch = peak_locator.run_batch(time_samples=dataset.x_values, signal=dataset.signals)
Plot the results
batch.plot_histogram_counts()
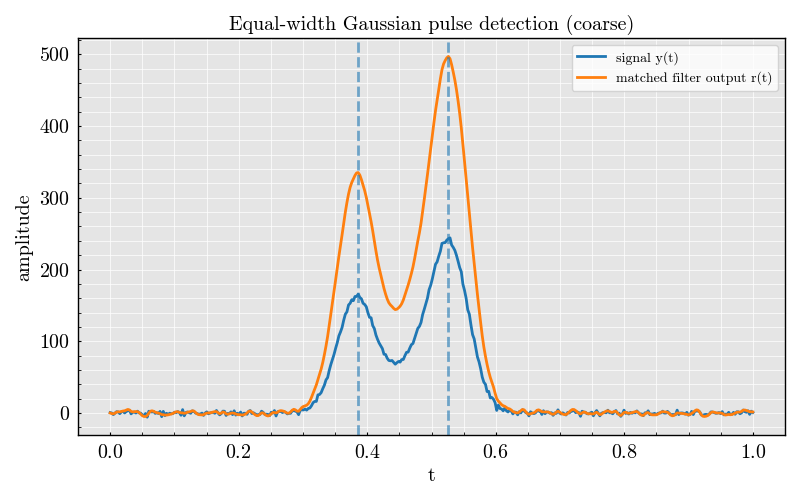
<Figure size 500x340 with 1 Axes>
Plot the results
batch.plot(ncols=3, max_plots=6, true_position=dataset.positions, show_kernel=True)
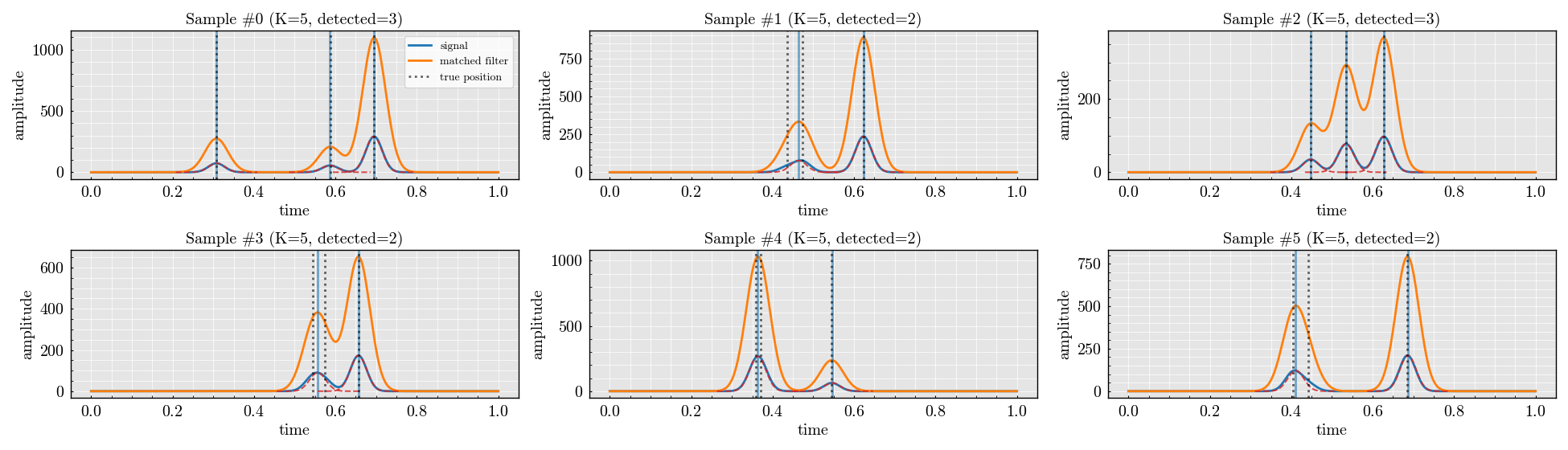
<Figure size 1950x560 with 6 Axes>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 1.128 seconds)