Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Sphere Particles: 1#
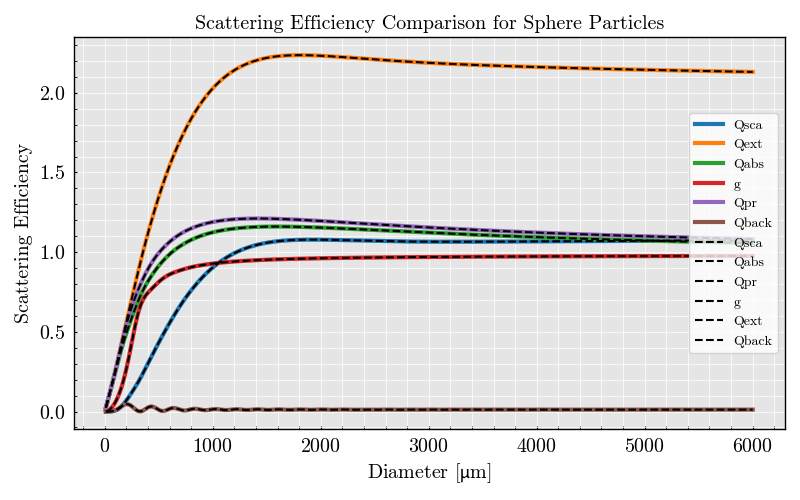
# Standard library imports
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PyMieSim.units import ureg
# PyMieSim imports
from PyMieSim.experiment.scatterer import Sphere
from PyMieSim.experiment.source import Gaussian
from PyMieSim.experiment import Setup
from PyMieSim.directories import validation_data_path
from MPSPlots.styles import mps
# Define parameters
wavelength = 632.8 * ureg.nanometer # Wavelength of the source in meters
index = (1.4 + 0.2j) * ureg.RIU # Refractive index of the sphere
medium_index = 1.2 * ureg.RIU # Refractive index of the medium
optical_power = 1 * ureg.watt # Power of the light source in watts
NA = 0.2 * ureg.AU # Numerical aperture
diameters = (
np.geomspace(10, 6_000, 800) * ureg.nanometer
) # Diameters from 10 nm to 6 μm
# Configure the Gaussian source
source = Gaussian(
wavelength=wavelength,
polarization=0 * ureg.degree,
optical_power=optical_power,
NA=NA,
)
# Setup spherical scatterer
scatterer = Sphere(
diameter=diameters, refractive_index=index, medium_refractive_index=medium_index, source=source
)
# Create experimental setup
experiment = Setup(scatterer=scatterer, source=source)
comparison_measures = ["Qsca", "Qext", "Qabs", "g", "Qpr", "Qback"]
# Compute PyMieSim scattering efficiency data
pymiesim = experiment.get(*comparison_measures, as_numpy=True)
pymiescatt_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
validation_data_path / "pymiescatt/example_shpere_1.csv"
)
# Plot results
with plt.style.context(mps):
figure, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1)
pymiescatt_dataframe.diameter *= 1e9
for string in comparison_measures:
ax.plot(
pymiescatt_dataframe["diameter"],
pymiescatt_dataframe[string],
label="PyMieScatt: " + string,
linewidth=3,
)
for data, string in zip(pymiesim, comparison_measures):
ax.plot(
diameters.to(ureg.nanometer).magnitude,
data,
label="PyMieSim: " + string,
linestyle="--",
color="black",
linewidth=1.5,
)
ax.set(
xlabel=r"Diameter [$\mu$m]",
ylabel="Scattering Efficiency",
title="Scattering Efficiency Comparison for Sphere Particles",
)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.501 seconds)
