Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Example: eigenmodes 2#
In this example, we calculate and visualize the eigenmodes of a finite difference operator combined with a circular mesh potential. The boundary conditions, mesh properties, and eigenmode calculations are all set up for demonstration purposes.
Boundaries |
left |
right |
top |
bottom |
|---|---|---|---|---|
anti-sym |
zero |
zero |
zero |
Importing required packages#
Here we import the necessary libraries for numerical computations, rendering, and finite difference operations.
from scipy.sparse import linalg
from PyFinitDiff.finite_difference_2D import FiniteDifference, get_circular_mesh_triplet, Boundaries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PyFinitDiff import BoundaryValue
Setting up the finite difference instance and boundaries#
We define the grid size and set up the finite difference instance with specified boundary conditions.
n_y = n_x = 80
sparse_instance = FiniteDifference(
n_x=n_x,
n_y=n_y,
dx=1,
dy=1,
derivative=2,
accuracy=4,
boundaries=Boundaries(left=BoundaryValue.ANTI_SYMMETRIC)
)
triplet = sparse_instance.triplet
Creating the circular mesh potential#
We create a circular mesh triplet, specifying the inner and outer values, and offset parameters.
mesh_triplet = get_circular_mesh_triplet(
n_x=n_x,
n_y=n_y,
value_out=1.0,
value_in=1.4444,
x_offset=-100,
y_offset=0,
radius=70
)
Combining the finite difference and mesh triplets#
We add the circular mesh triplet to the finite difference Laplacian to form the dynamic triplet.
dynamic_triplet = sparse_instance.triplet + mesh_triplet
Calculating the eigenmodes#
We compute the first four eigenmodes of the combined operator using the scipy sparse linear algebra package.
eigen_values, eigen_vectors = linalg.eigs(
dynamic_triplet.to_scipy_sparse(),
k=4,
which='LM',
sigma=1.4444
)
shape = [sparse_instance.n_x, sparse_instance.n_y]
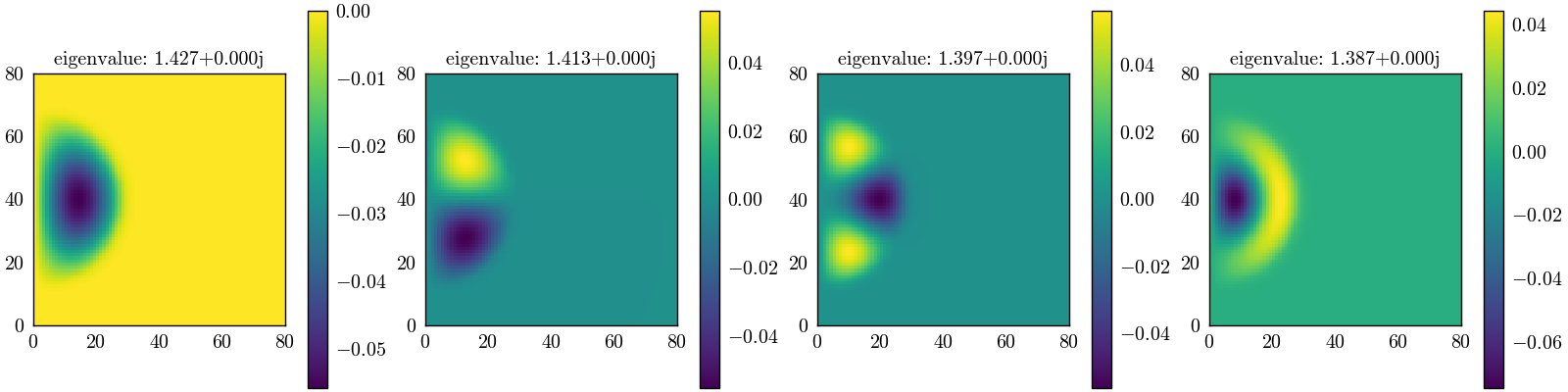
Visualizing the eigenmodes with matplotlib#
We visualize the first four eigenmodes by reshaping the eigenvectors and plotting them using matplotlib.
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 4, figsize=(16, 4), constrained_layout=True)
for i, ax in enumerate(axes):
vector = eigen_vectors[:, i].real.reshape(shape)
mesh = ax.pcolormesh(vector, shading='auto', cmap='viridis')
ax.set_title(f'eigenvalue: {eigen_values[i]:.3f}')
ax.set_aspect('equal')
plt.colorbar(mesh, ax=ax)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.061 seconds)