Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Flow Cytometry Simulation: Full System Example with Workflow#
This tutorial demonstrates a complete flow cytometry simulation using the FlowCyPy library. It models fluidics, optics, signal processing, and classification of multiple particle populations.
Steps Covered:#
Configure simulation parameters and noise models
Define laser source, flow cell geometry, and fluidics
Add synthetic particle populations
Set up detectors, amplifier, and digitizer
Simulate analog and digital signal acquisition
Apply triggering and peak detection
Classify particle events based on peak features
from FlowCyPy.workflow import (
ureg,
SimulationSettings,
Workflow,
Detector,
circuits,
peak_locator,
triggering_system,
distributions,
population,
GammaModel,
classifiers,
)
SimulationSettings.include_noises = False
SimulationSettings.include_shot_noise = True
SimulationSettings.include_dark_current_noise = True
SimulationSettings.include_source_noise = True
SimulationSettings.include_amplifier_noise = True
SimulationSettings.assume_perfect_hydrodynamic_focusing = True
SimulationSettings.population_cutoff_bypass = False
population_0 = population.Sphere(
name="Pop 0",
medium_refractive_index=distributions.Delta(1.33 * ureg.RIU),
concentration=5e10 * ureg.particle / ureg.milliliter,
diameter=distributions.RosinRammler(
shape=150 * ureg.nanometer,
scale=50 * ureg.nanometer,
low_cutoff=50.0 * ureg.nanometer,
),
refractive_index=distributions.Normal(
mean=1.44 * ureg.RIU,
standard_deviation=0.002 * ureg.RIU,
low_cutoff=1.33 * ureg.RIU,
),
)
population_1 = population.Sphere(
name="Pop 1",
medium_refractive_index=distributions.Delta(1.33 * ureg.RIU),
concentration=5e17 * ureg.particle / ureg.milliliter,
diameter=distributions.RosinRammler(
shape=50 * ureg.nanometer,
scale=50 * ureg.nanometer,
),
refractive_index=distributions.Normal(
mean=1.44 * ureg.RIU,
standard_deviation=0.002 * ureg.RIU,
low_cutoff=1.33 * ureg.RIU,
),
sampling_method=GammaModel(mc_samples=10_000),
)
detector_0 = Detector(
name="side",
phi_angle=90 * ureg.degree,
numerical_aperture=0.3 * ureg.AU,
responsivity=1 * ureg.ampere / ureg.watt,
)
detector_1 = Detector(
name="forward",
phi_angle=0 * ureg.degree,
numerical_aperture=0.3 * ureg.AU,
responsivity=1 * ureg.ampere / ureg.watt,
)
discriminator = triggering_system.DynamicWindow(
trigger_detector_name="forward",
threshold="2sigma",
pre_buffer=20,
post_buffer=20,
)
peak_locator = peak_locator.GlobalPeakLocator(compute_width=False)
analog_processing = [
circuits.BaselineRestorator(window_size=10 * ureg.microsecond),
circuits.BesselLowPass(cutoff=2 * ureg.megahertz, order=4, gain=2),
]
workflow = Workflow(
wavelength=405 * ureg.nanometer,
source_numerical_aperture=0.1 * ureg.AU,
optical_power=200 * ureg.milliwatt,
sample_volume_flow=80 * ureg.microliter / ureg.minute,
sheath_volume_flow=1 * ureg.milliliter / ureg.minute,
width=200 * ureg.micrometer,
height=100 * ureg.micrometer,
populations=[population_0, population_1],
gain=10 * ureg.volt / ureg.ampere,
bandwidth=10 * ureg.megahertz,
bit_depth="14bit",
sampling_rate=60 * ureg.megahertz,
saturation_levels="auto",
background_power=0.001 * ureg.milliwatt,
detectors=[detector_0, detector_1],
analog_processing=analog_processing,
trigger=discriminator,
peak_locator=peak_locator,
)
workflow.initialize()
run_record = workflow.run(run_time=1 * ureg.millisecond)
_ = run_record.event_collection.plot(x="Diameter")
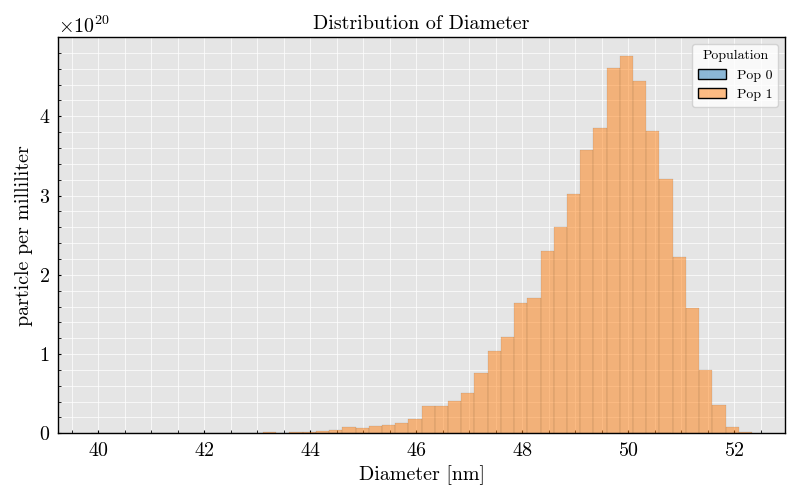
Step 5: Plot Events and Raw Analog Signals#
_ = run_record.event_collection.plot(x="forward")
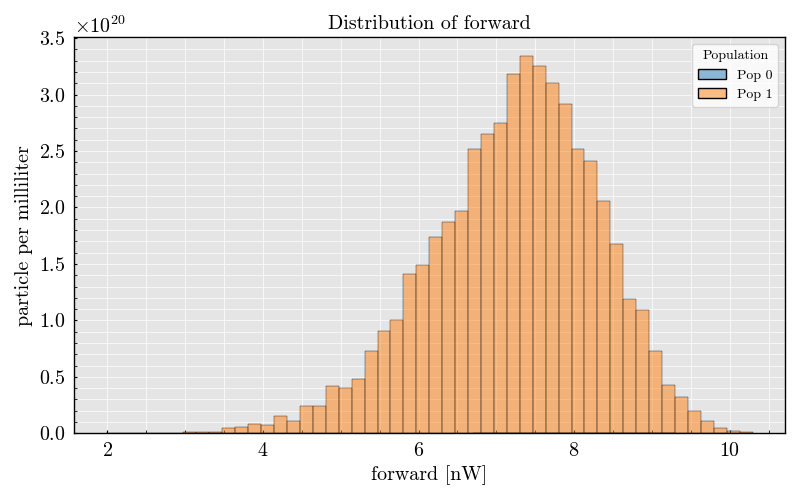
Plot raw analog signals#
_ = run_record.plot_analog(figure_size=(12, 8))
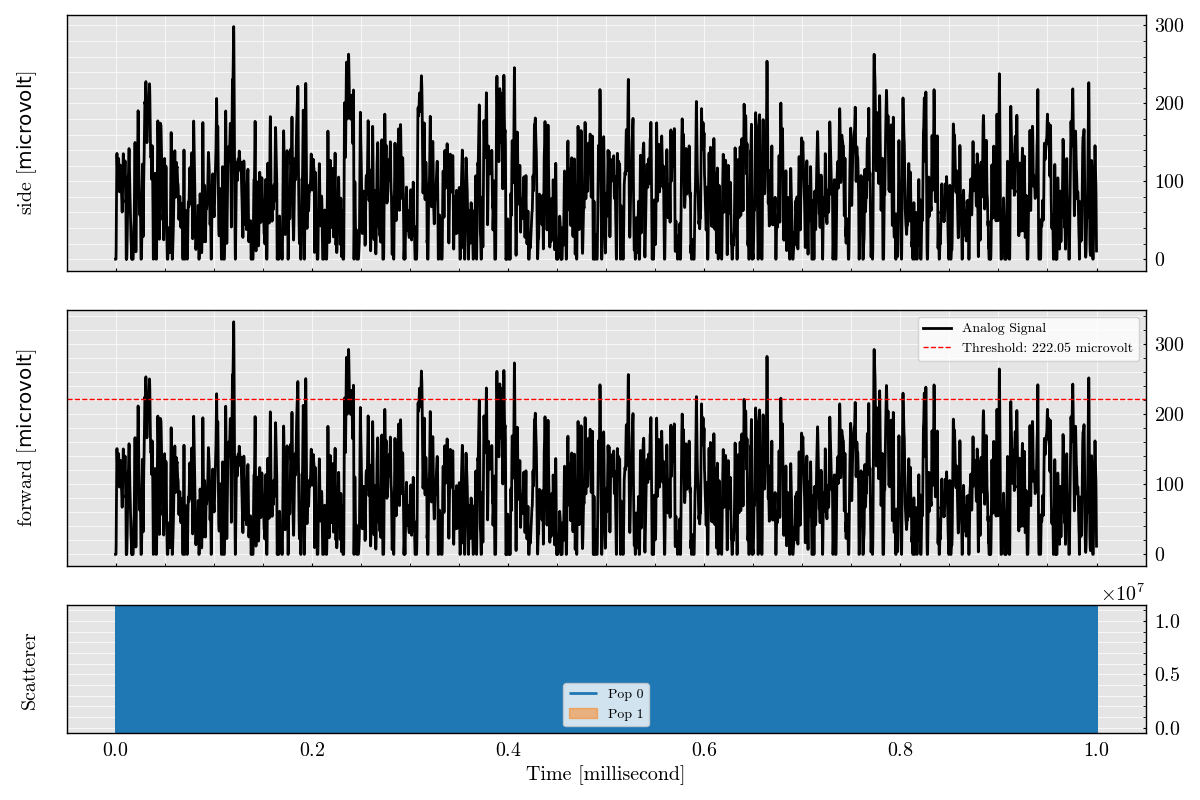
Step 6: Plot Triggered Analog Segments#
_ = run_record.plot_digital(figure_size=(12, 8))
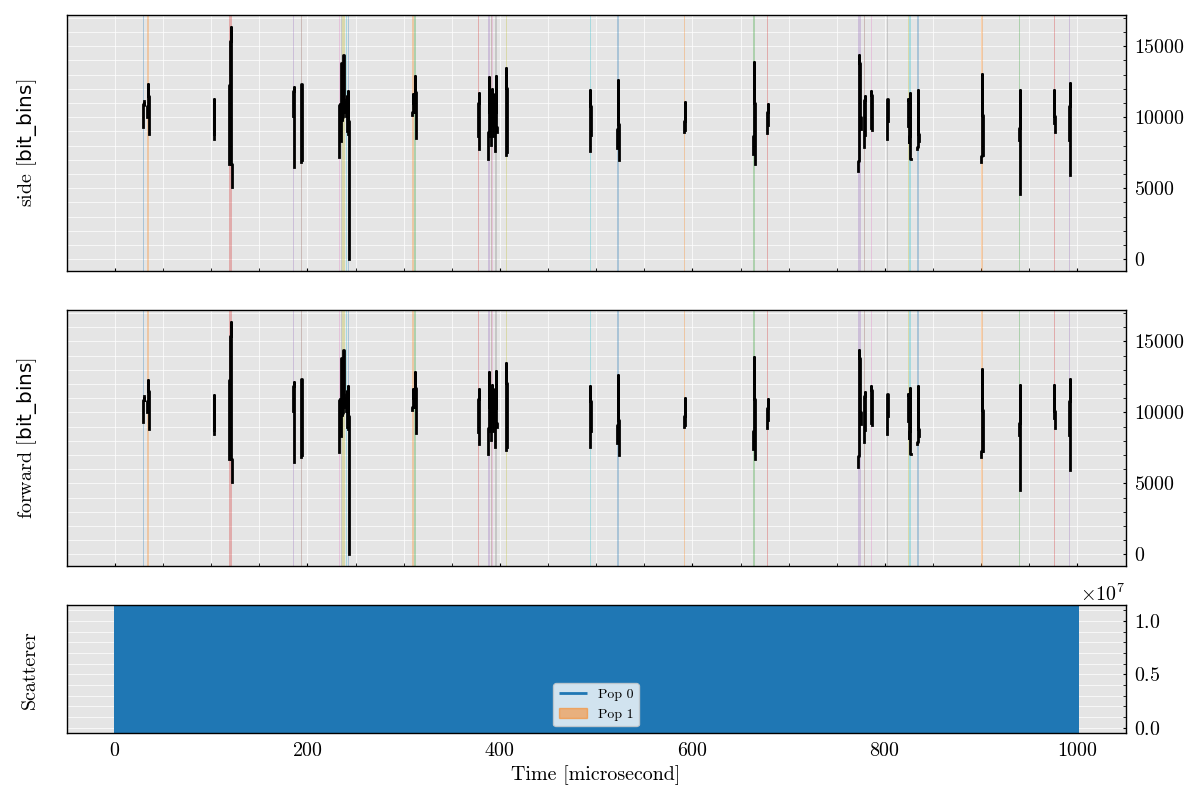
Step 7: Plot Peak Features#
_ = run_record.peaks.plot(x=("forward", "Height"))
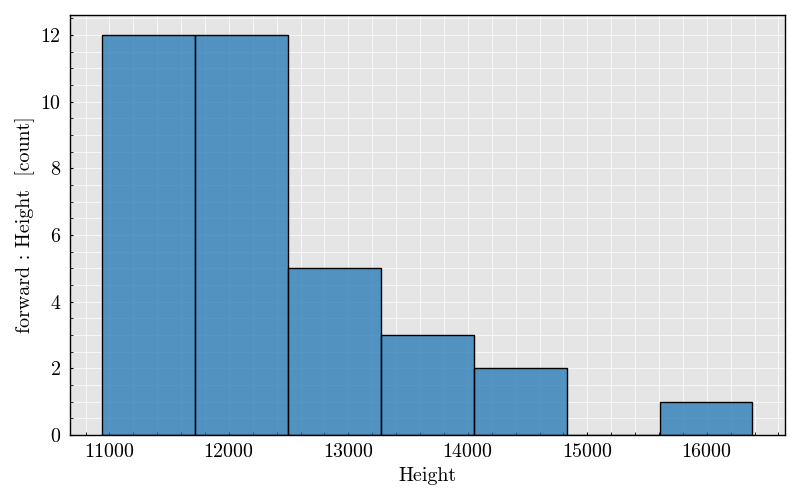
Step 8: Classify Events from Peak Features#
classifier = classifiers.KmeansClassifier(number_of_clusters=2)
classified = classifier.run(
dataframe=run_record.peaks.unstack("Detector"),
features=["Height"],
detectors=["side", "forward"],
)
_ = classified.plot(x=("side", "Height"), y=("forward", "Height"))
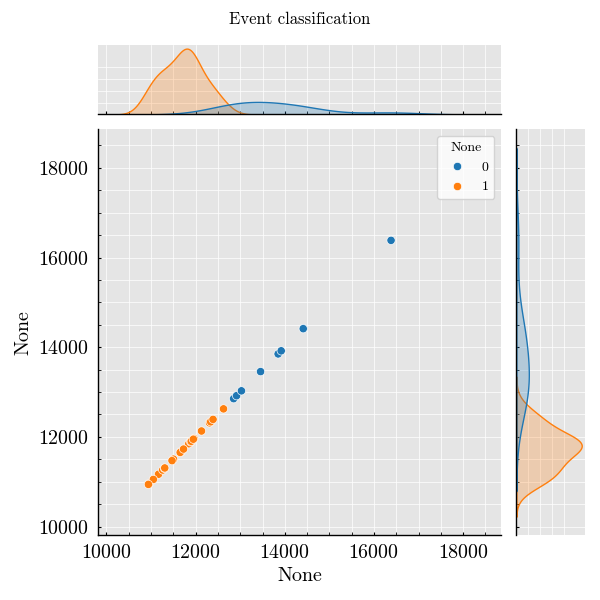
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 48.117 seconds)