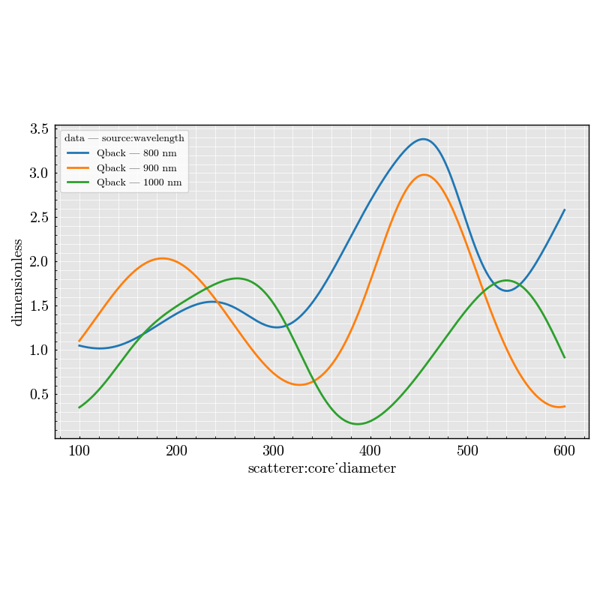
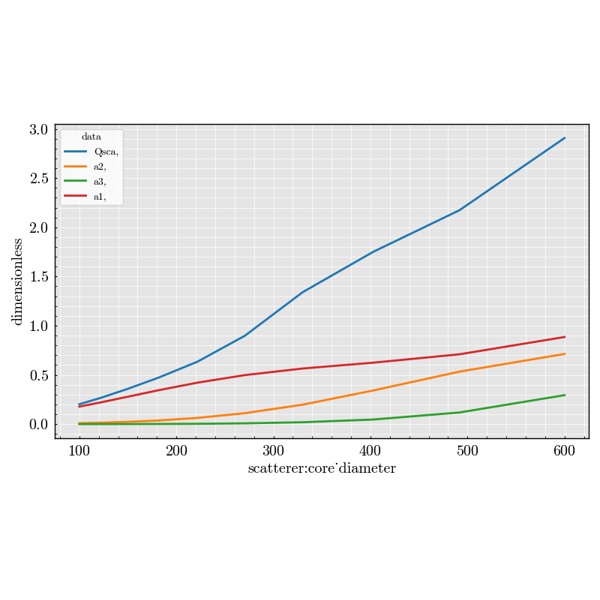
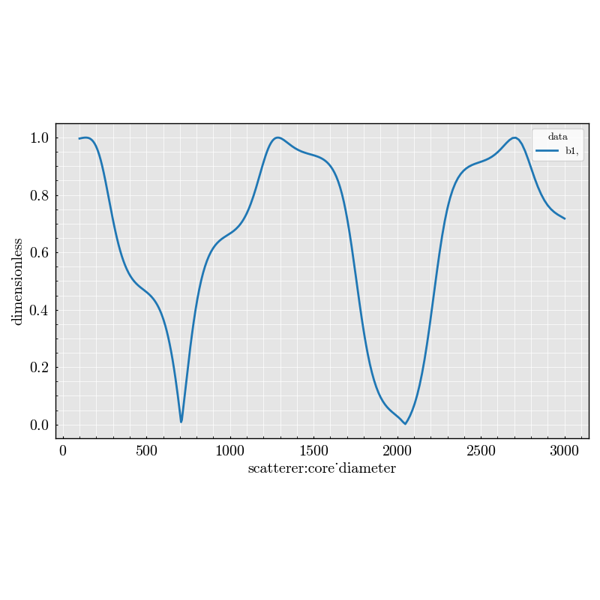
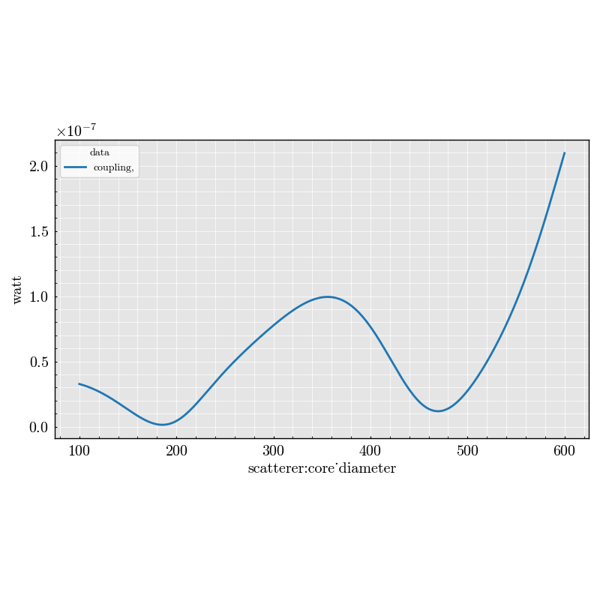
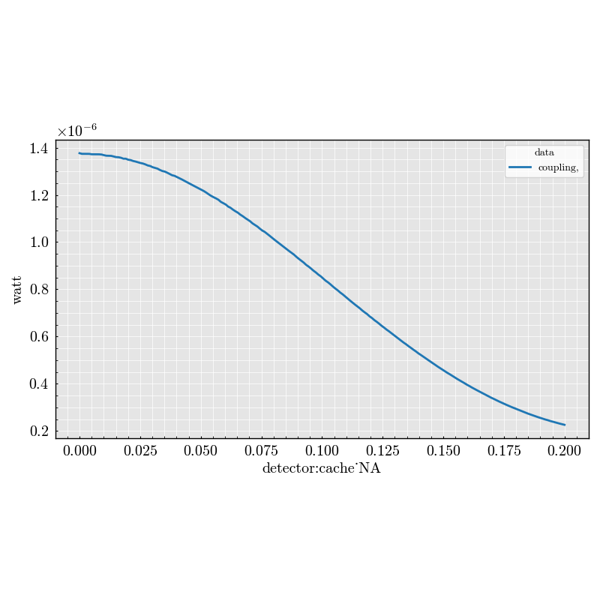
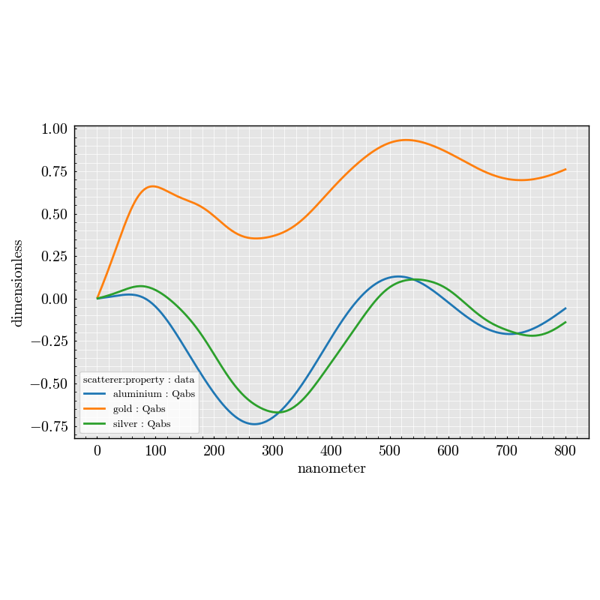
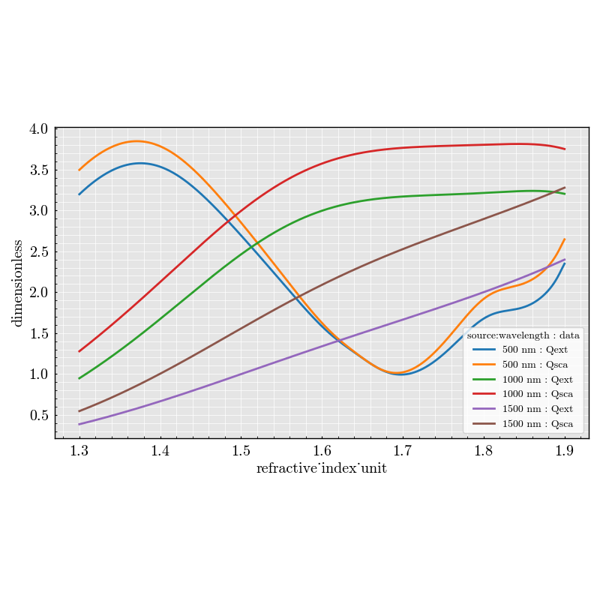
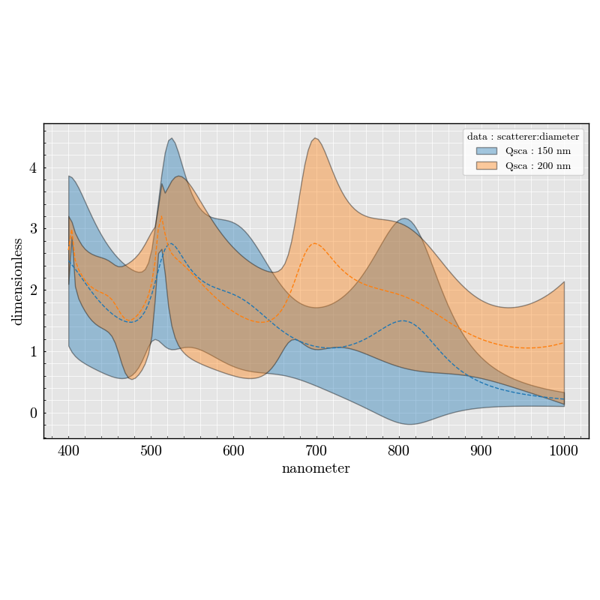
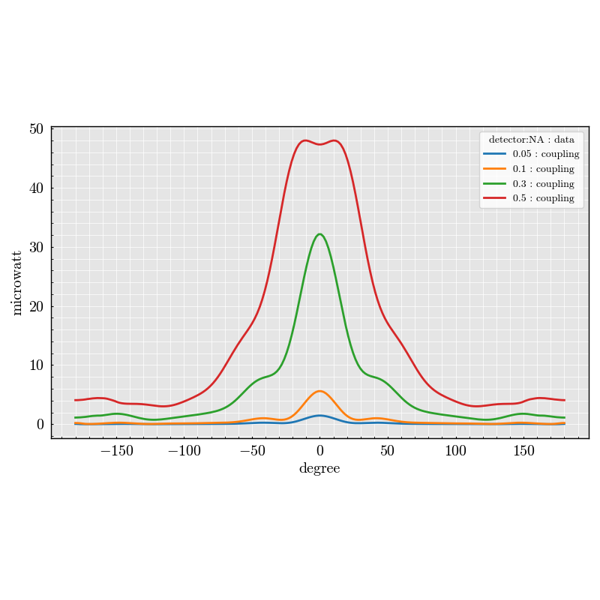
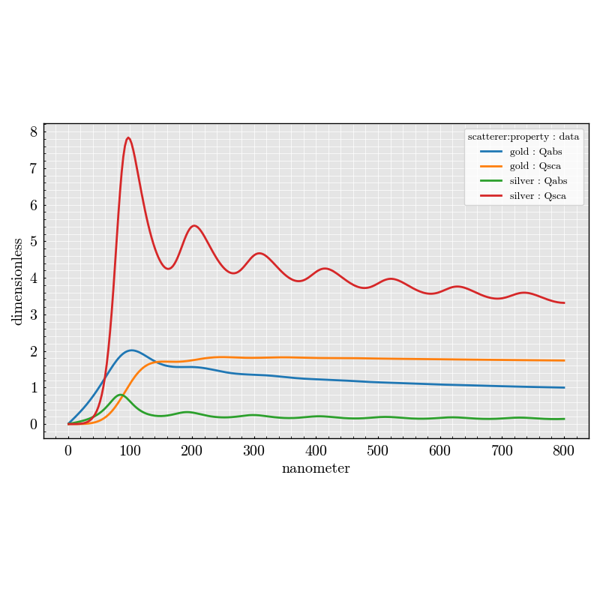
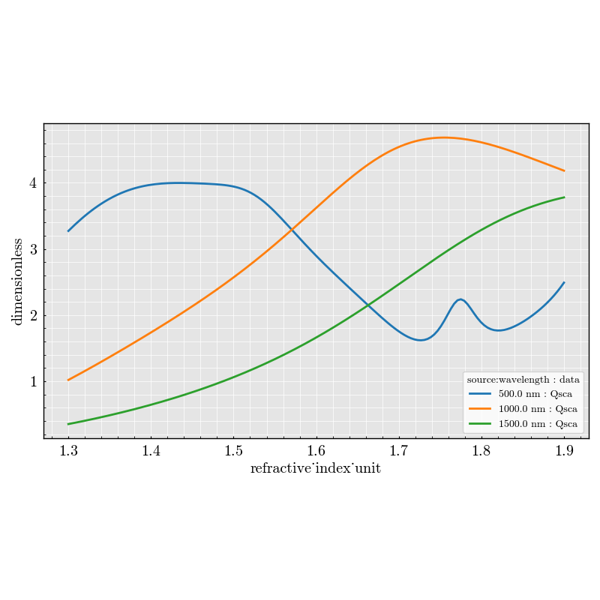
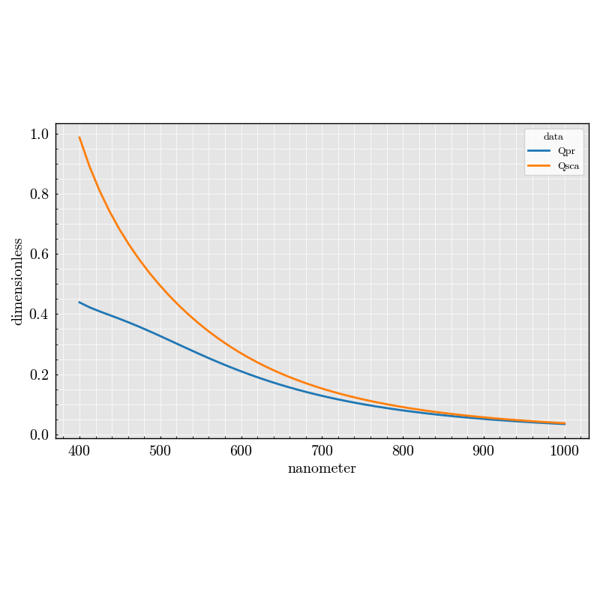
Experiment Module#
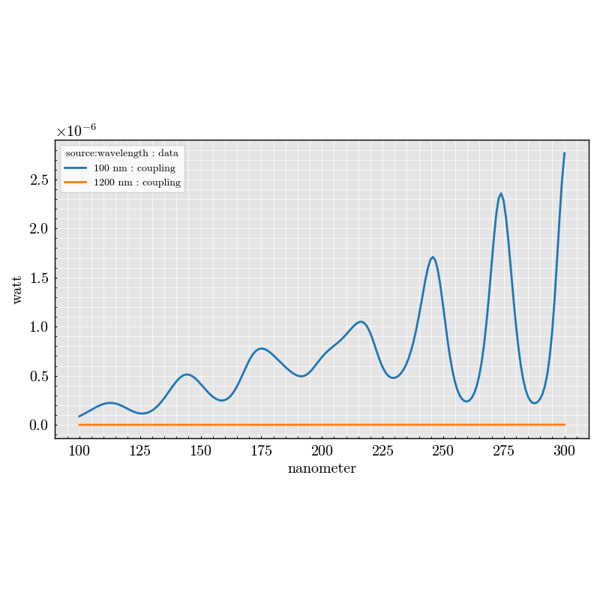
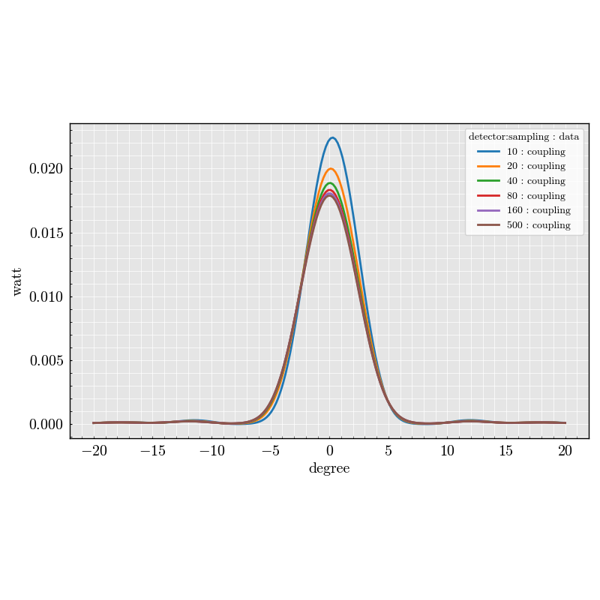
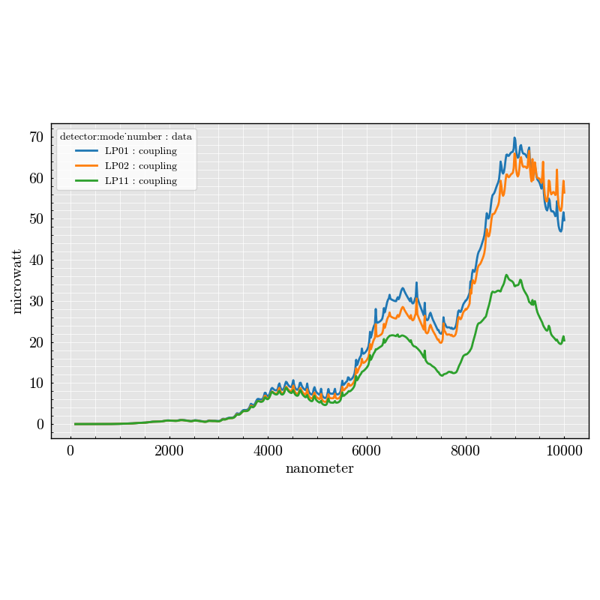
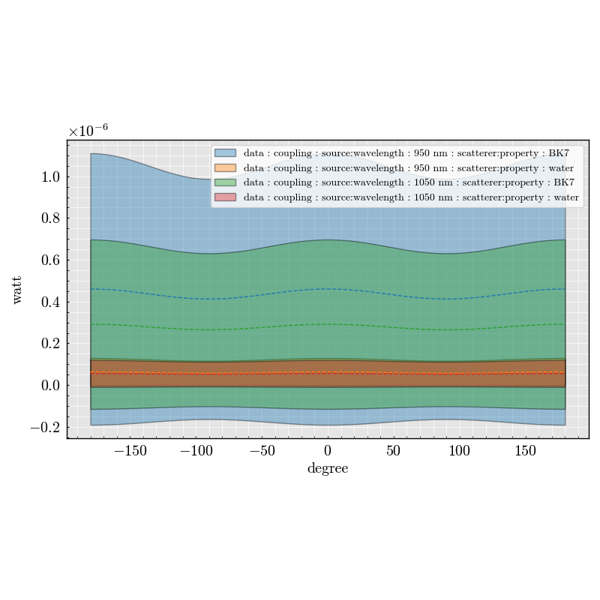
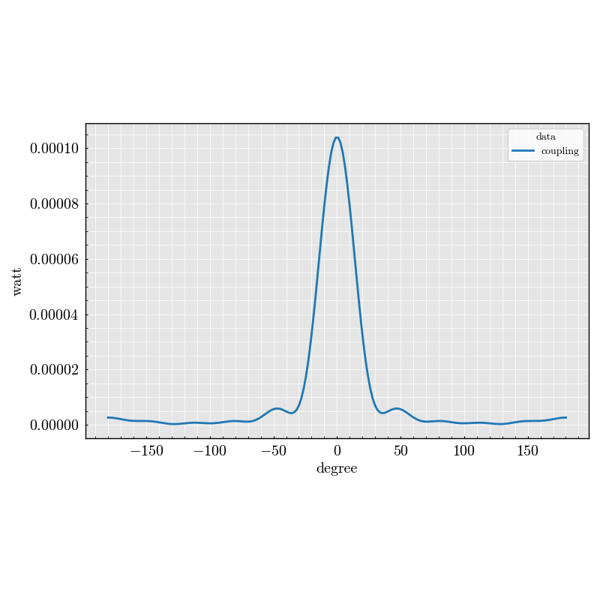
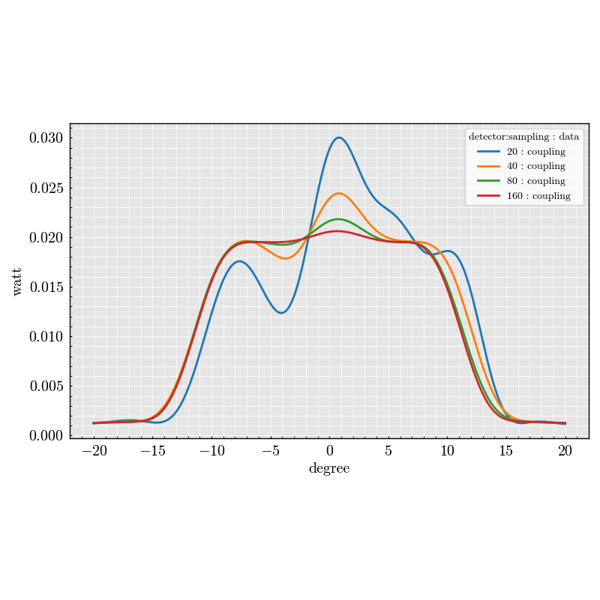
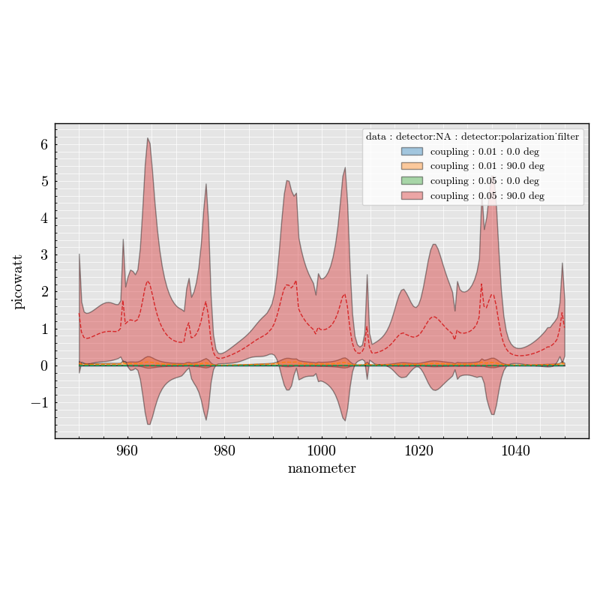
The experiment package is used to build large parameter sweeps. It lets you
combine sources, scatterers and detectors to explore how scattering quantities
change across many configurations.
Core-Shell#
Examples of particles composed of a core and shell.
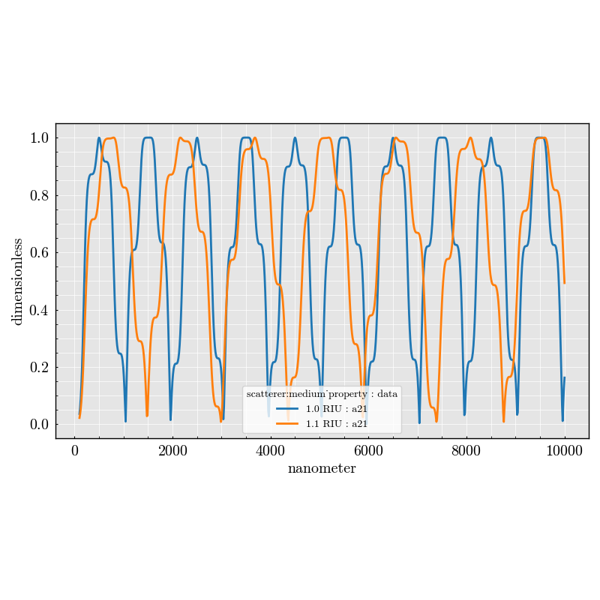
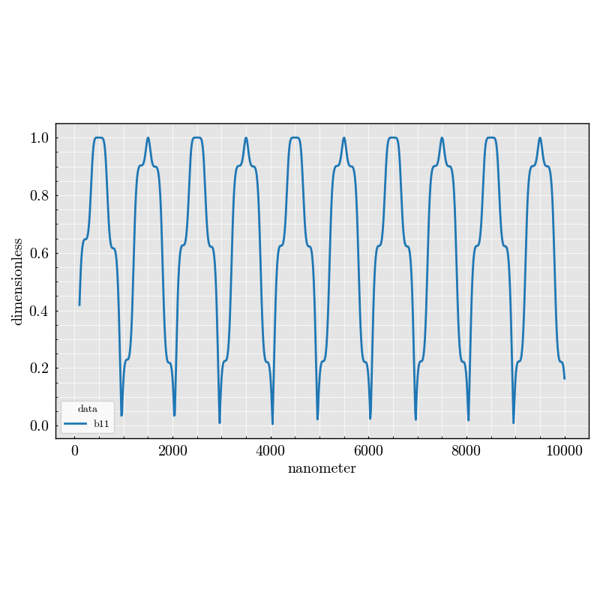
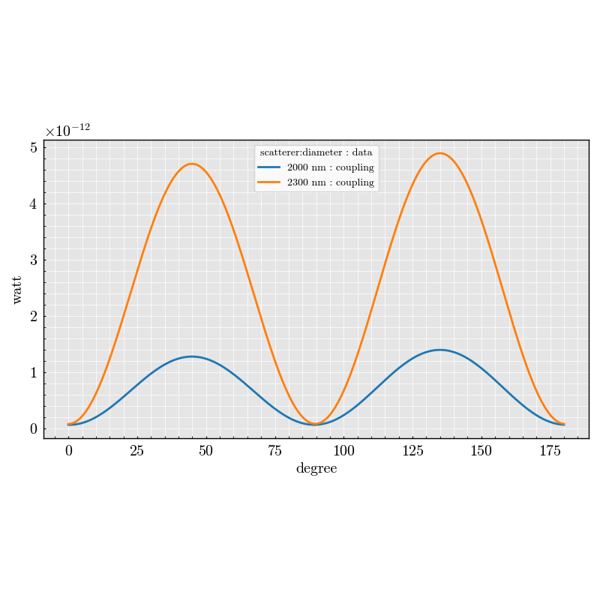
Cylinder#
Examples demonstrating infinite cylindrical scatterers.
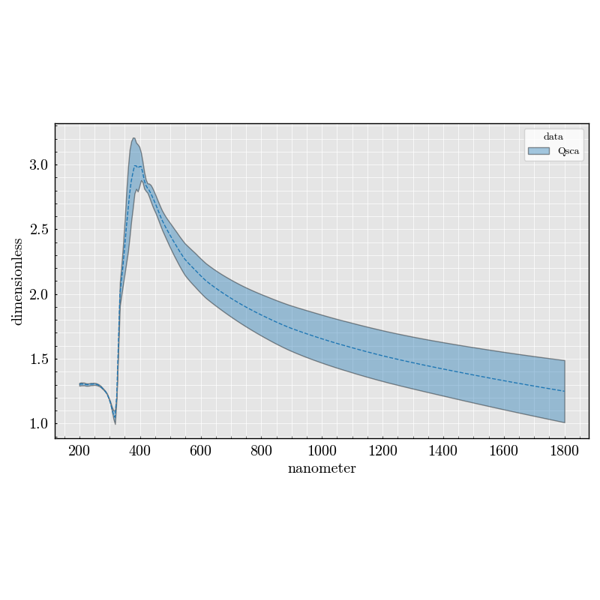
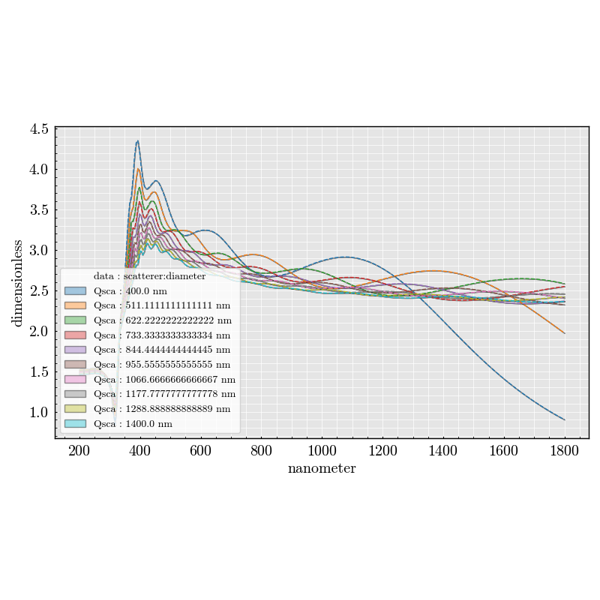
Sphere#
Examples focused on spherical scatterers.