Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Sphere: Coherent Goniometer#
Importing the package dependencies: numpy, PyMieSim
import numpy
from PyMieSim.units import ureg
from PyMieSim.experiment.detector import CoherentMode
from PyMieSim.experiment.scatterer import Sphere
from PyMieSim.experiment.source import Gaussian
from PyMieSim.experiment import Setup
from PyOptik import Material
source = Gaussian(
wavelength=1200 * ureg.nanometer,
polarization=90 * ureg.degree,
optical_power=1e-3 * ureg.watt,
NA=0.2 * ureg.AU,
)
scatterer = Sphere(
diameter=2000 * ureg.nanometer,
refractive_index=Material.BK7,
medium_refractive_index=1 * ureg.RIU,
source=source,
)
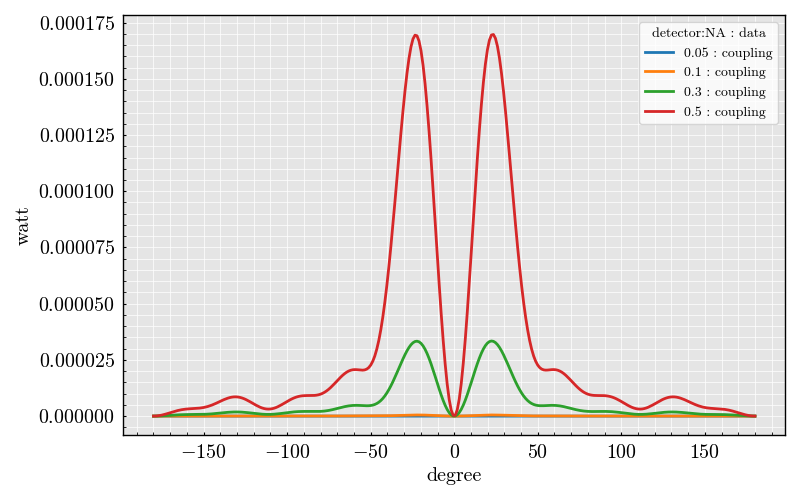
detector = CoherentMode(
mode_number="LP11",
NA=[0.5, 0.3, 0.1, 0.05] * ureg.AU,
phi_offset=numpy.linspace(-180, 180, 300) * ureg.degree,
gamma_offset=0 * ureg.degree,
sampling=400 * ureg.AU,
polarization_filter=10 * ureg.degree,
rotation=0 * ureg.degree, # Rotation of the mode field
)
experiment = Setup(scatterer=scatterer, source=source, detector=detector)
dataframe = experiment.get("coupling")
dataframe.plot(x="detector:phi_offset")
<Figure size 800x500 with 1 Axes>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.567 seconds)
