Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
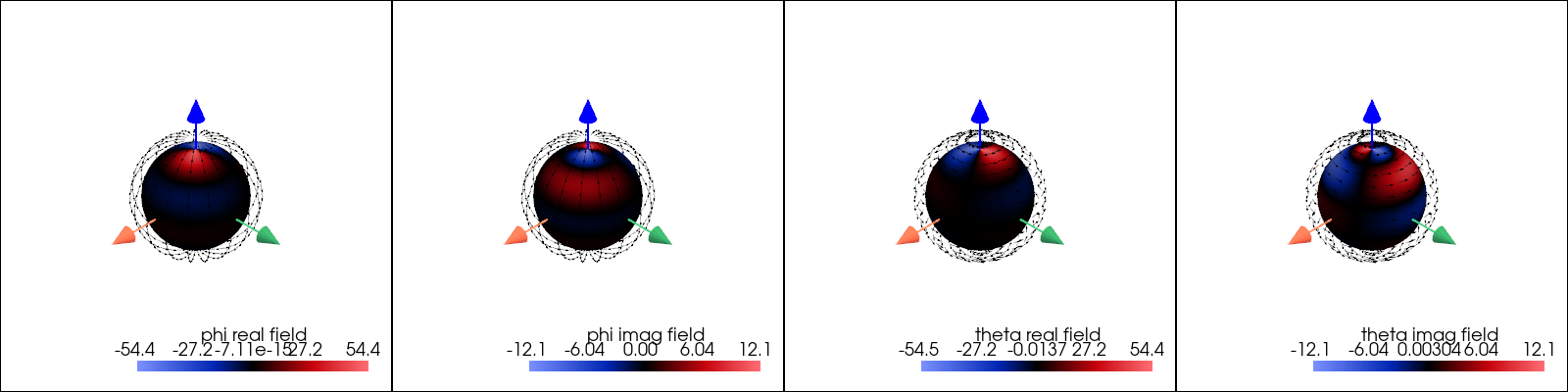
Far-Fields Computation and Visualization#
This example demonstrates the process of computing and visualizing the far-fields of a scatterer using PyMieSim.
Importing the package: PyMieSim
from PyMieSim.single.scatterer import Sphere
from PyMieSim.single.source import Gaussian
from PyMieSim.units import nanometer, degree, watt, AU, RIU
Defining the source
source = Gaussian(
wavelength=1000 * nanometer, # 1000 nm
polarization=30 * degree, # Right circular polarization
optical_power=1 * watt, # Arbitrary units
NA=0.3 * AU # Numerical Aperture
)
Defining the scatterer
scatterer = Sphere(
diameter=1500 * nanometer, # 1500 nm
source=source,
property=1.4 * RIU, # Refractive index of the scatterer
medium_property=1.0 * RIU # Refractive index of the surrounding medium
)
Computing the data
data = scatterer.get_far_field(sampling=100) # Specify the number of sampling points
Plotting the data
figure = data.plot()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.768 seconds)
