Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Near-Fields Computation and Visualization#
This example demonstrates the process of computing and visualizing the far-fields of a scatterer using PyMieSim.
Importing the package: PyMieSim
from PyMieSim.units import ureg
from PyMieSim.single.scatterer import Sphere
from PyMieSim.single.source import Gaussian
from PyMieSim.single.representations import NearField
source = Gaussian(
wavelength=300 * ureg.nanometer,
polarization=0 * ureg.degree,
optical_power=1 * ureg.watt,
NA=0.3 * ureg.AU,
)
scatterer = Sphere(
diameter=400 * ureg.nanometer,
source=source,
refractive_index=(1.4 + 0.j) * ureg.RIU,
medium_refractive_index=1. * ureg.RIU,
)
near_field = NearField(
scatterer=scatterer,
)
near_field.plot(
"Ex:real",
"Ex:abs",
type="total",
plane_origin=(0.0, 0.0, 0.0),
plane_normal=(0.0, 1.0, 0.0),
sampling=400,
extent_scale=4,
tight_layout=True,
)
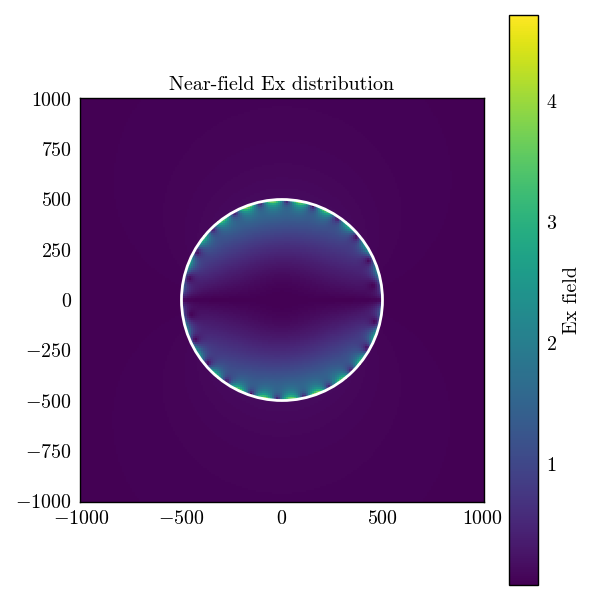
Computing total near field component: Ex
/opt/hostedtoolcache/Python/3.11.14/x64/lib/python3.11/site-packages/PyMieSim/single/representations/near_field.py:249: UnitStrippedWarning: The unit of the quantity is stripped when downcasting to ndarray.
fields[component] = numpy.asarray(values).reshape(self.X.shape)
<Figure size 1200x600 with 4 Axes>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 13.827 seconds)
